Ansible + FreeBSD
Install ansible on master/parent
After a default installation of FreeBSD on master. We immediately install python and ansible.
root@master:~# pkg install lang/python
root@master:~# pkg install ansible
Updating FreeBSD repository catalogue...
FreeBSD repository is up-to-date.
All repositories are up-to-date.
The following 11 packages will be affected (of 0 checked):
New packages to be INSTALLED:
ansible: 1.8.4
py27-pycrypto: 2.6.1_1
gmp: 5.1.3_2
py27-setuptools27: 5.5.1_1
py27-paramiko: 1.14.0
py27-ecdsa: 0.11_1
py27-yaml: 3.11
py27-Jinja2: 2.7.3
py27-MarkupSafe: 0.23
py27-Babel: 1.3_2
py27-pytz: 2014.10,1
The process will require 31 MiB more space.
5 MiB to be downloaded.
Proceed with this action? [y/N]: y
Fetching ansible-1.8.4.txz: 100% 1 MiB 275.7kB/s 00:04
...
Checking integrity... done (0 conflicting)
[1/11] Installing py27-setuptools27-5.5.1_1...
[1/11] Extracting py27-setuptools27-5.5.1_1: 100%
[2/11] Installing gmp-5.1.3_2...
[2/11] Extracting gmp-5.1.3_2: 100%
[3/11] Installing py27-pytz-2014.10,1...
[3/11] Extracting py27-pytz-2014.10,1: 100%
[4/11] Installing py27-pycrypto-2.6.1_1...
[4/11] Extracting py27-pycrypto-2.6.1_1: 100%
[5/11] Installing py27-ecdsa-0.11_1...
[5/11] Extracting py27-ecdsa-0.11_1: 100%
[6/11] Installing py27-MarkupSafe-0.23...
[6/11] Extracting py27-MarkupSafe-0.23: 100%
[7/11] Installing py27-Babel-1.3_2...
[7/11] Extracting py27-Babel-1.3_2: 100%
[8/11] Installing py27-paramiko-1.14.0...
[8/11] Extracting py27-paramiko-1.14.0: 100%
[9/11] Installing py27-yaml-3.11...
[9/11] Extracting py27-yaml-3.11: 100%
[10/11] Installing py27-Jinja2-2.7.3...
[10/11] Extracting py27-Jinja2-2.7.3: 100%
[11/11] Installing ansible-1.8.4...
[11/11] Extracting ansible-1.8.4: 100%
Message for ansible-1.8.4:
===============================================================================
To use Ansible, you need at least a host database.
If you installed examples, you will have a sample
host database and a sample configuration file:
/usr/local/share/examples/ansible/hosts
/usr/local/share/examples/ansible/ansible.cfg
To use Ansible to control systems other than FreeBSD,
set the Python interpreter in the host database for
that system. Example:
[freebsd]
host1
host2
[centos]
host3
host4
[centos:vars]
ansible_python_interpreter=/usr/bin/python
===============================================================================
Hosts
We add dlt-server in our ansible hosts
root@master:/usr/local/etc/ansible # vi hosts
127.0.0.1
dlt-server
To ensure our ansible master can ping our child node, we add it to our /etc/hosts and ping
root@master:/usr/local/etc/ansible # vi /etc/hosts
192.168.4.215 dlt-server
Setup a child server (dlt-server)
This assumes we have a default FreeBSD10.1 child server which we will call dlt-server.
SSH Setup
Allow root login
% vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
PermitRootLogin yes
% /etc/rc.d/sshd restart
Allow master to have password less access to the node via SSH. On master copy the ssh keys to the node machine
% scp -r server_keys.tar.gz root@dlt-server:/root/
% ssh root@dlt-server
% cd /root
% tar -zxvf server_keys.tar.gz
% mv ssh_keys .ssh
Let’s test if the keys work. On master,
% ssh root@dlt-server
root@dlt-server:~ #
Install Python on child server
Ansible needs python, we can install python on the child itself
root@dlt-server:~ # pkg install lang/python
...
root@dlt-server:~ # which python
/usr/local/bin/python
root@bsd10dev1:~ # python --version
Python 2.7.9
But let’s use ansible. We use the line below courtesy of http://lampros.chaidas.com/index.php/2014/06/23/bootstrapping-pkg-and-installing-python-on-a-freebsd-target-via-ansible/ and https://dan.langille.org/2013/12/06/bootstrapping-installing-pkg-on-freebsd-unattended-and-without-answering-yes/
root@master:~# ansible dlt-server -u root -m raw -a 'env ASSUME_ALWAYS_YES=YES pkg bootstrap'
Now we install python thru ansible
root@master:~# ansible dlt-server -u root -m raw -a 'env ASSUME_ALWAYS_YES=YES pkg install lang/python'
dlt-server | success | rc=0 >>
Updating FreeBSD repository catalogue...
Fetching meta.txz: 100% 944 B 0.9kB/s 00:01
Fetching packagesite.txz: 100% 5 MiB 213.9kB/s 00:25
Processing entries: 100%
FreeBSD repository update completed. 24086 packages processed
Updating database digests format: 100%
The following 6 packages will be affected (of 0 checked):
New packages to be INSTALLED:
python: 2.7_2,2
python27: 2.7.9
libffi: 3.2.1
indexinfo: 0.2.2
gettext-runtime: 0.19.4
python2: 2_3
The process will require 66 MiB more space.
10 MiB to be downloaded.
Fetching python-2.7_2,2.txz: 100% 992 B 1.0kB/s 00:01
Fetching python27-2.7.9.txz: 100% 10 MiB 82.1kB/s 02:08
Fetching libffi-3.2.1.txz: 100% 35 KiB 36.2kB/s 00:01
Fetching indexinfo-0.2.2.txz: 100% 5 KiB 5.0kB/s 00:01
Fetching gettext-runtime-0.19.4.txz: 100% 146 KiB 29.8kB/s 00:05
Fetching python2-2_3.txz: 100% 1 KiB 1.1kB/s 00:01
Checking integrity... done (0 conflicting)
[1/6] Installing indexinfo-0.2.2...
[1/6] Extracting indexinfo-0.2.2: 100%
[2/6] Installing libffi-3.2.1...
[2/6] Extracting libffi-3.2.1: 100%
[3/6] Installing gettext-runtime-0.19.4...
[3/6] Extracting gettext-runtime-0.19.4: 100%
[4/6] Installing python27-2.7.9...
[4/6] Extracting python27-2.7.9: 100%
[5/6] Installing python2-2_3...
[5/6] Extracting python2-2_3: 100%
[6/6] Installing python-2.7_2,2...
[6/6] Extracting python-2.7_2,2: 100%
Message for python27-2.7.9:
=====================================================================
Note that some standard Python modules are provided as separate ports
as they require additional dependencies. They are available as:
bsddb databases/py-bsddb
gdbm databases/py-gdbm
sqlite3 databases/py-sqlite3
tkinter x11-toolkits/py-tkinter
=====================================================================
Cool. Now let’s try a simple ping command, since we have python installed already.
root@master:~ # ansible dlt-server -m ping
dlt-server | success >> {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
Using a Playbook
We will now install freebsd packages (i.e git) thru ansible using pkgng http://docs.ansible.com/pkgng_module.html.
Our simple bootstrap playbook containing an install git task only
# bootstrap.yml for installing git,vim,bash
- name: boostrap
hosts: dlt-server
user: root
tasks:
- name: install git
pkgng: name=git
Run the playbook
# ansible-playbook bootstrap.yml
PLAY [boostrap] ***************************************************************
GATHERING FACTS ***************************************************************
ok: [dlt-server]
TASK: [install git] ***********************************************************
changed: [dlt-server]
PLAY RECAP ********************************************************************
dlt-server : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0
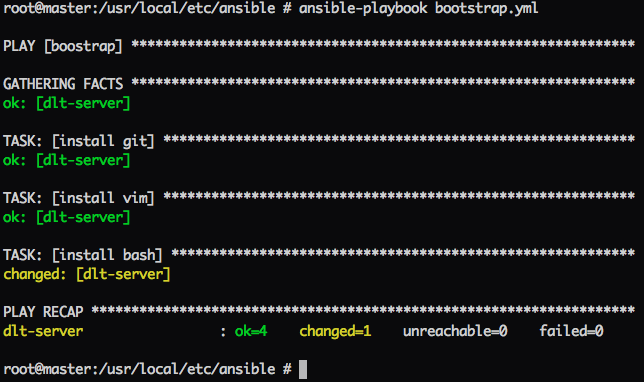
If we add vim and bash to the playbook
# bootstrap.yml for installing git,vim,bash
- name: boostrap
hosts: dlt-server
user: root
tasks:
- name: install git
pkgng: name=git
- name: install vim
pkgng: name=vim
- name: install bash
pkgng: name=bash
If you run the playbook again, the tasks that already run before will just be a green “ok”.